32 bit float
Previously, a sound recording file was deemed to be of good quality if it was a WAV file sampled at 44.1, 48 or 96 kHz with a resolution of 24 bit. Except when recording music, 48 kHz is usually enough.
In simple terms that means that audio is sampled 48,000 times per second, and the audio signal is given a number (amplitude value) between 1 and 16,777,216. In terms of decibels, this gives a recording dynamic range of 144 decibels (dB).
With a 24 bit recorder, the recording level must be set correctly. If the recording level is too loud, the audio will be distorted, because it will be at a level that cannot be defined. A recording that is too quiet can be made louder using a computer app, but the level of unwanted noise will also be increased as the wanted audio level is increased.
24 bit recording is much more tolerant of low level recording than a 16 bit recording, but it is still important to set the recording level correctly.
The enormous dynamic range of a 32 bit float recording means that you do not have to set the recording level at all. Every recording will be recorded at the optimal level and can be adjusted to the optimum playback level after the recording has been made, without any loss of quality. "Normalisation" is the process of adjusting the already recorded audio to the optimum playback level.
Some of the current 32 bit recorders will export normalised 24 bit audio files directly from the device, or the audio files can be normalised and converted to 24 bit using a computer.
Recording Level
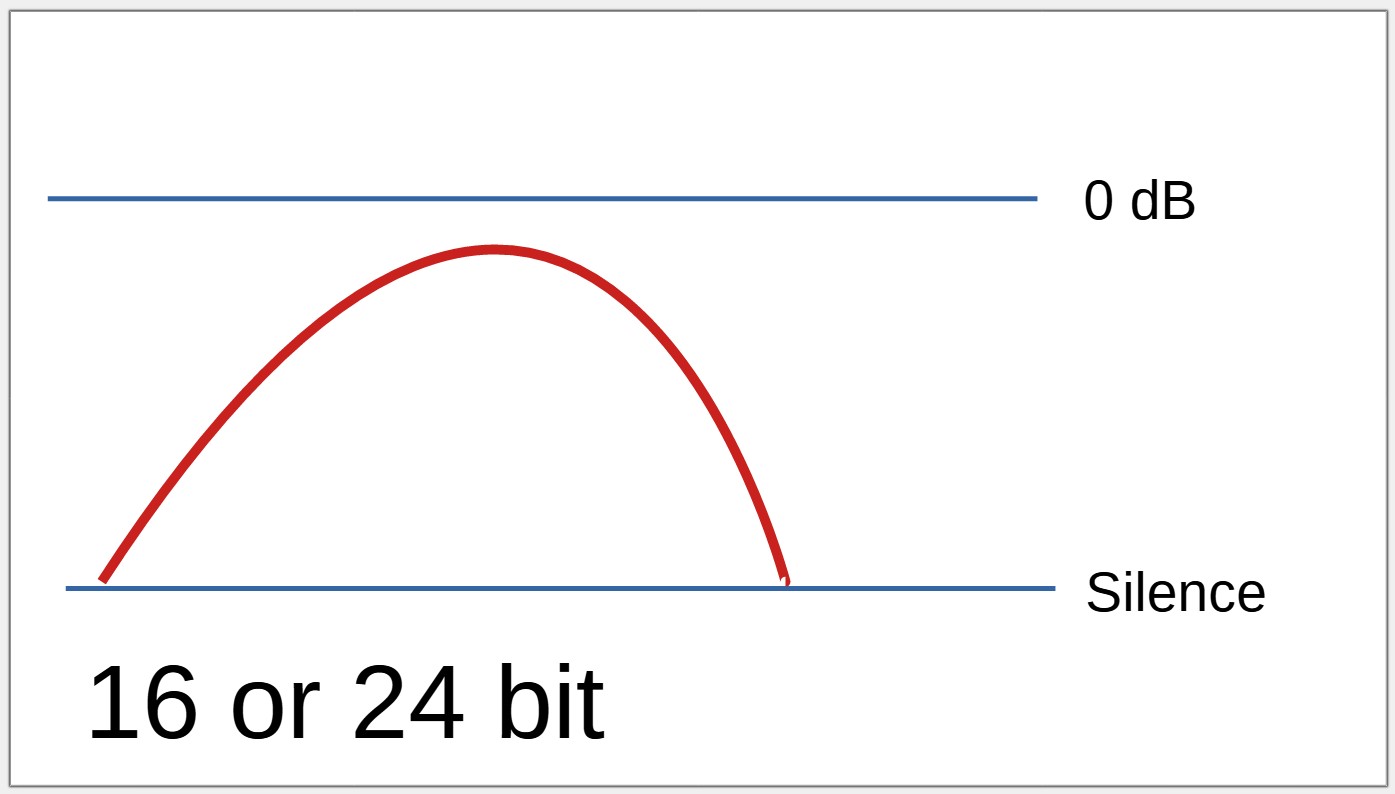
A digital recorder using 16 or 24 bit resolution has a limited volume range that can be recorded.
Audio that is recorded too quietly will have compromised quality.
Audio that is recorded too loudly will have audible distortion.
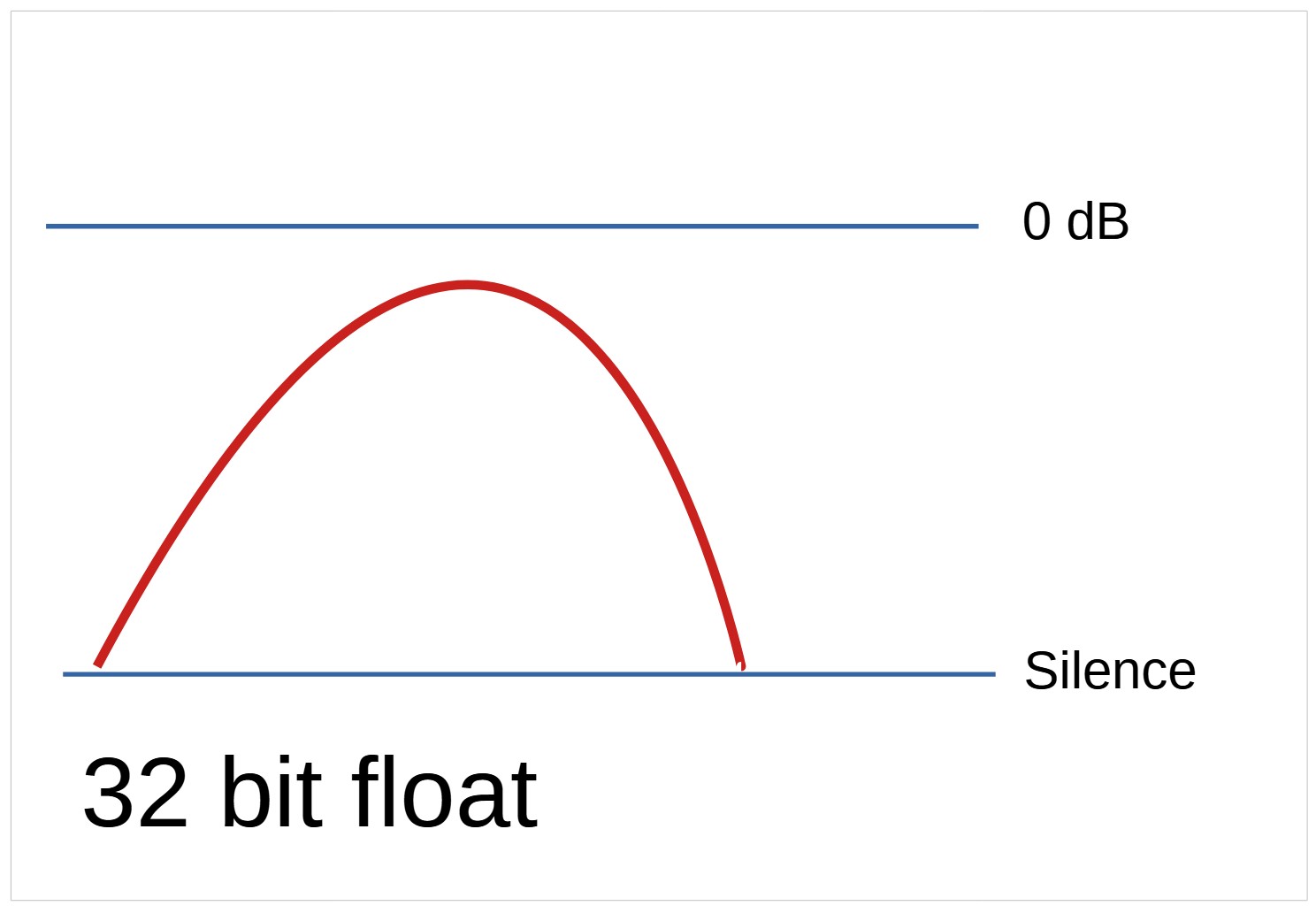
The increased dynamic range of a 32 bit float recording means recordings levels do not need to be set and recordings can be adjusted later using a computer app without loss of quality.
Optimal recording level
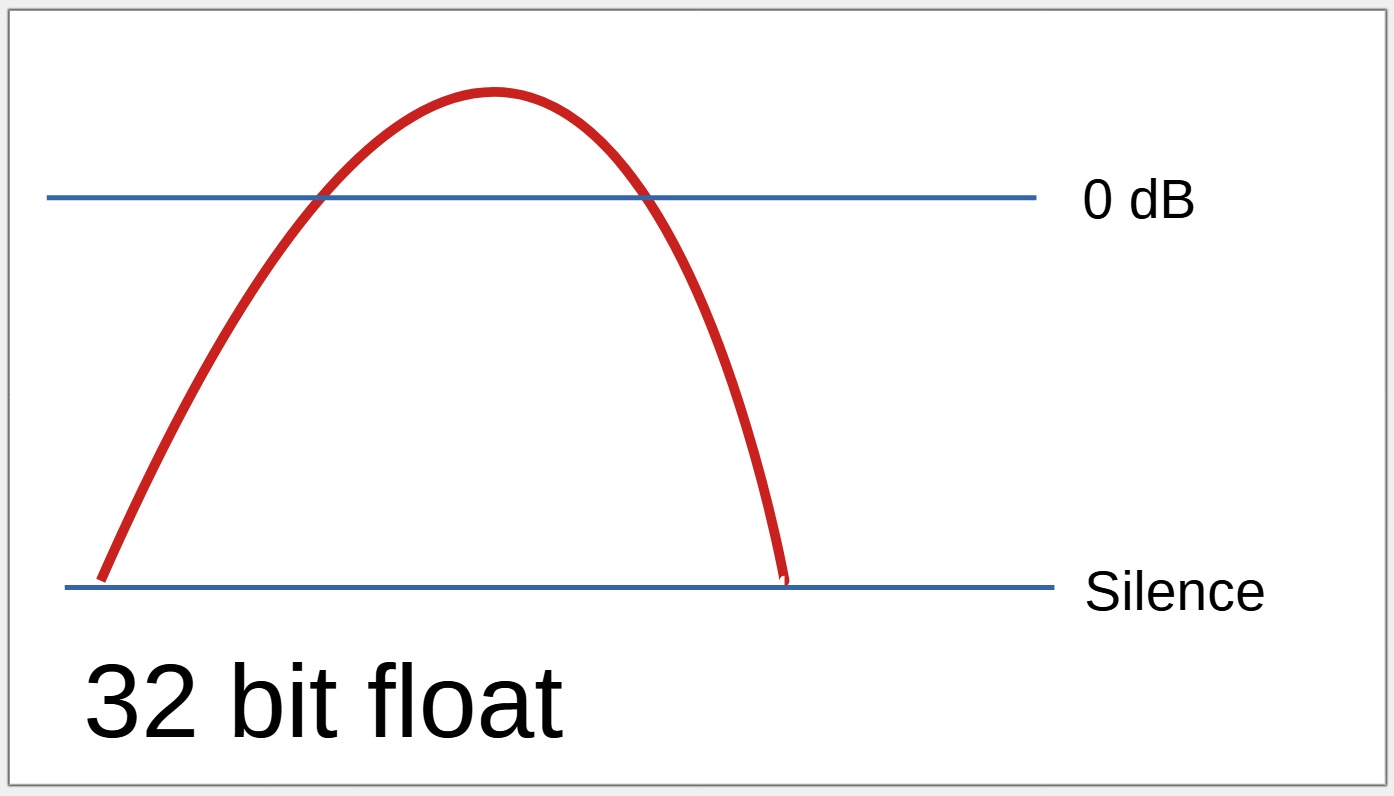
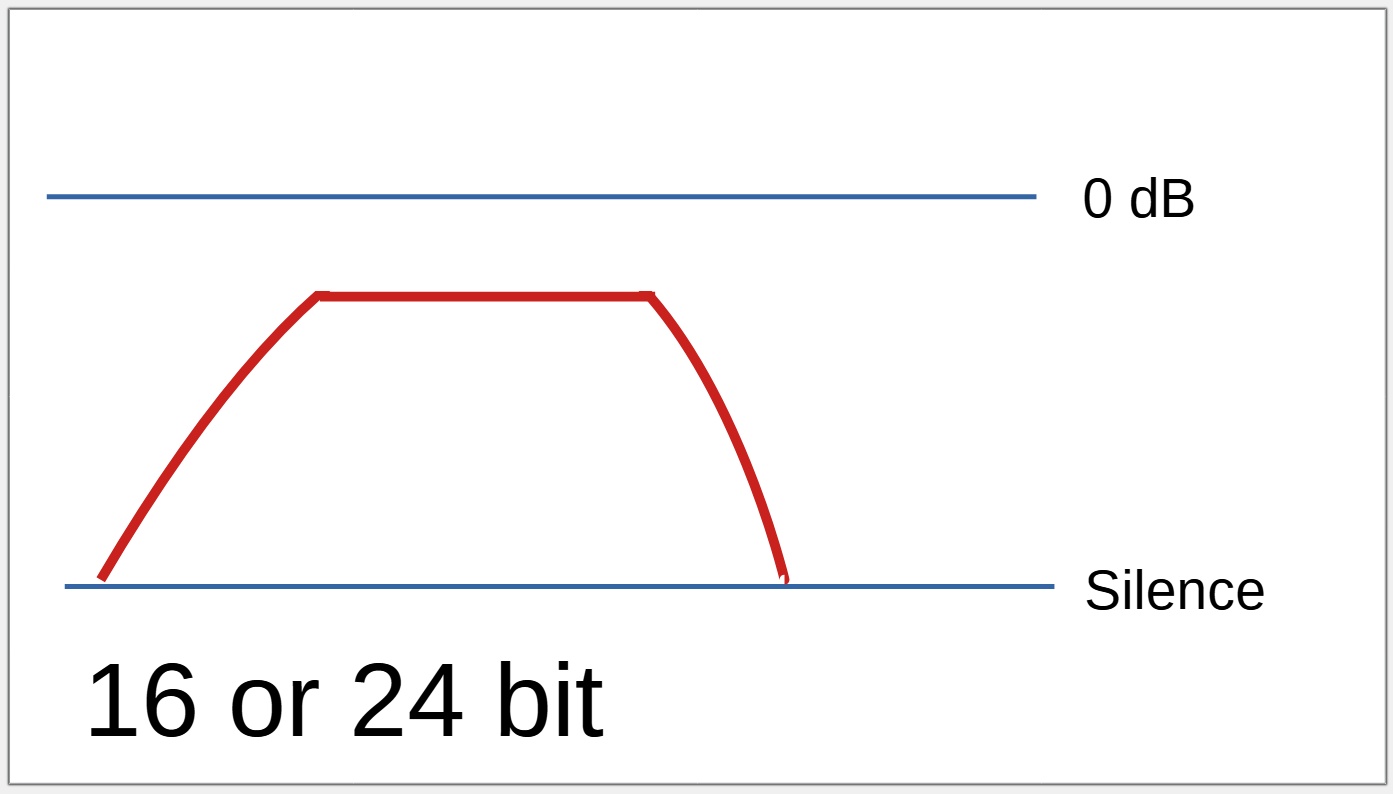
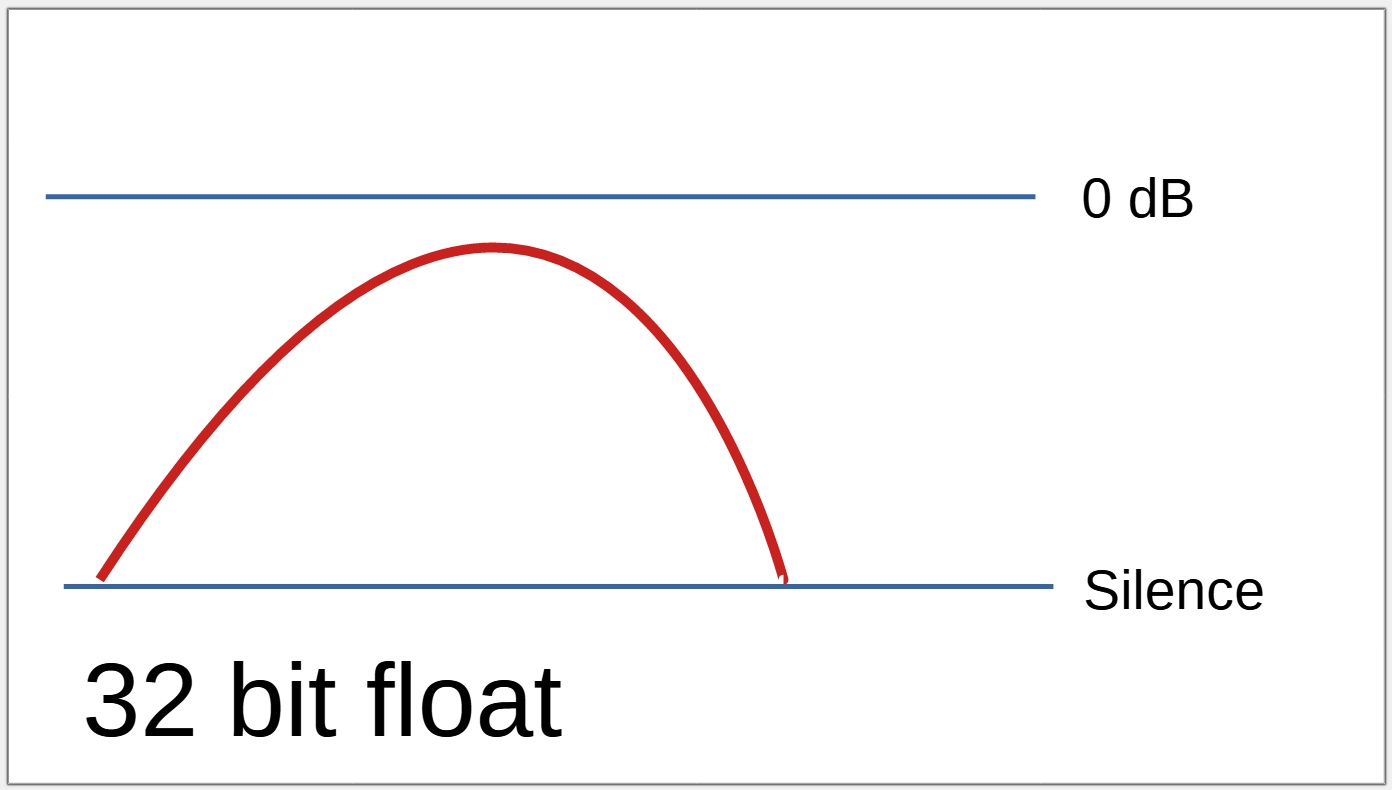
When a recording is loud
Recording above 0 dB is not possible with a 16 or 24 bit device.
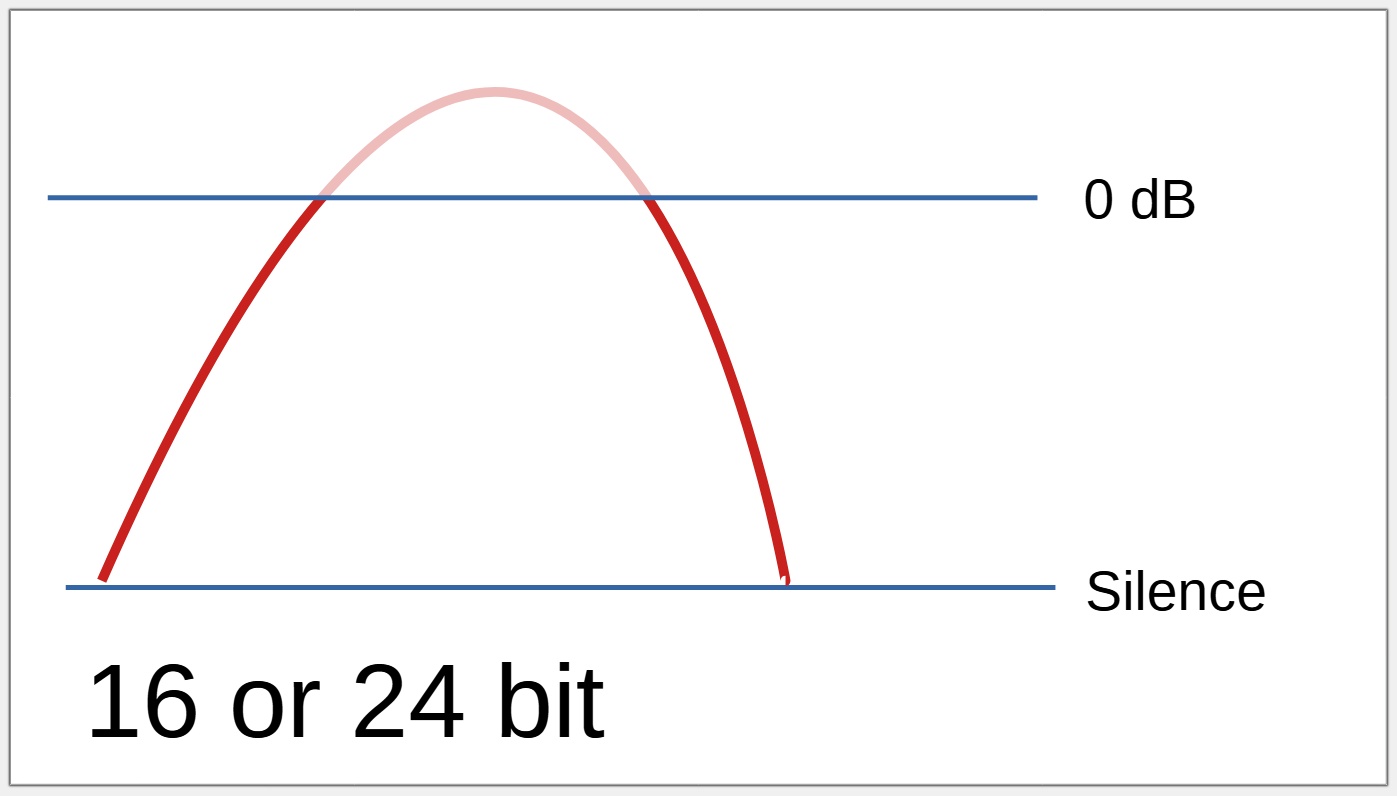
With a 16 or 24 bit recorder, no audio above 0 dB will actually be recorded, resulting in audible distortion.
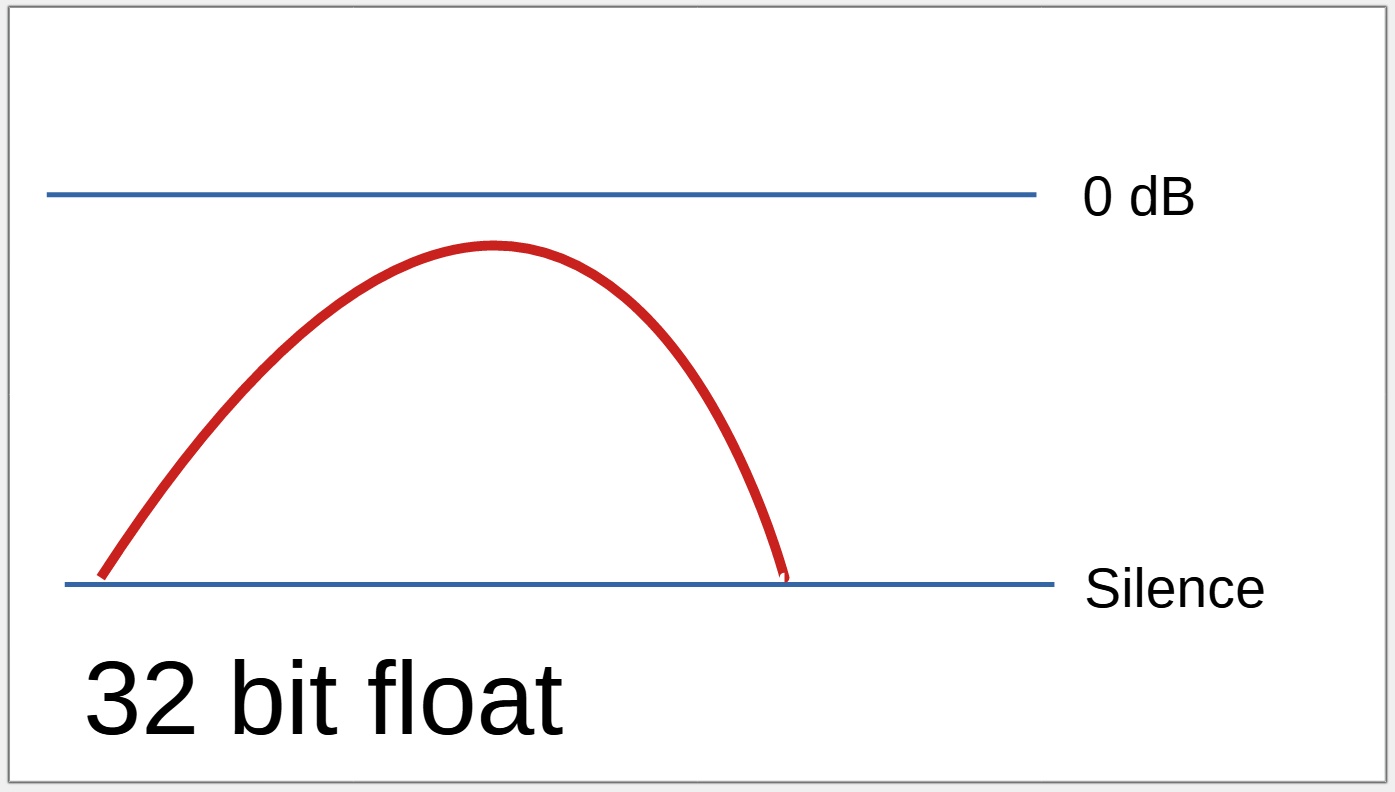
A 32 bit float recording can record hundreds of decibels below or above 0 dB.
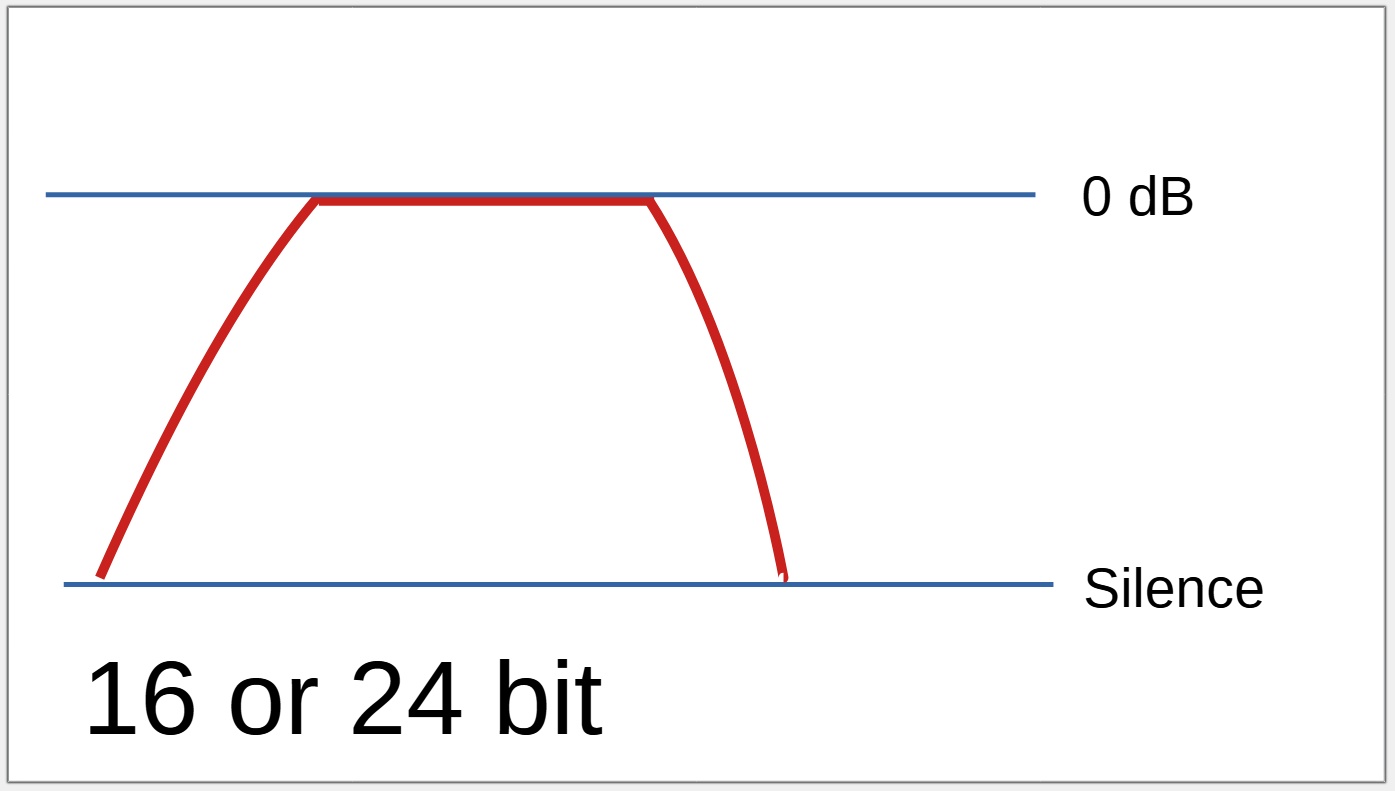

Even when the "too loud" recording level is lowered, the audio that was not able to be recorded on the 16 /24 bit device will still sound distorted, but the adjusted audio recorded using 32 bit float will sound perfect.
When a recording is soft
A recoding that is too soft will need to have the level increased, using normalisation or compression.
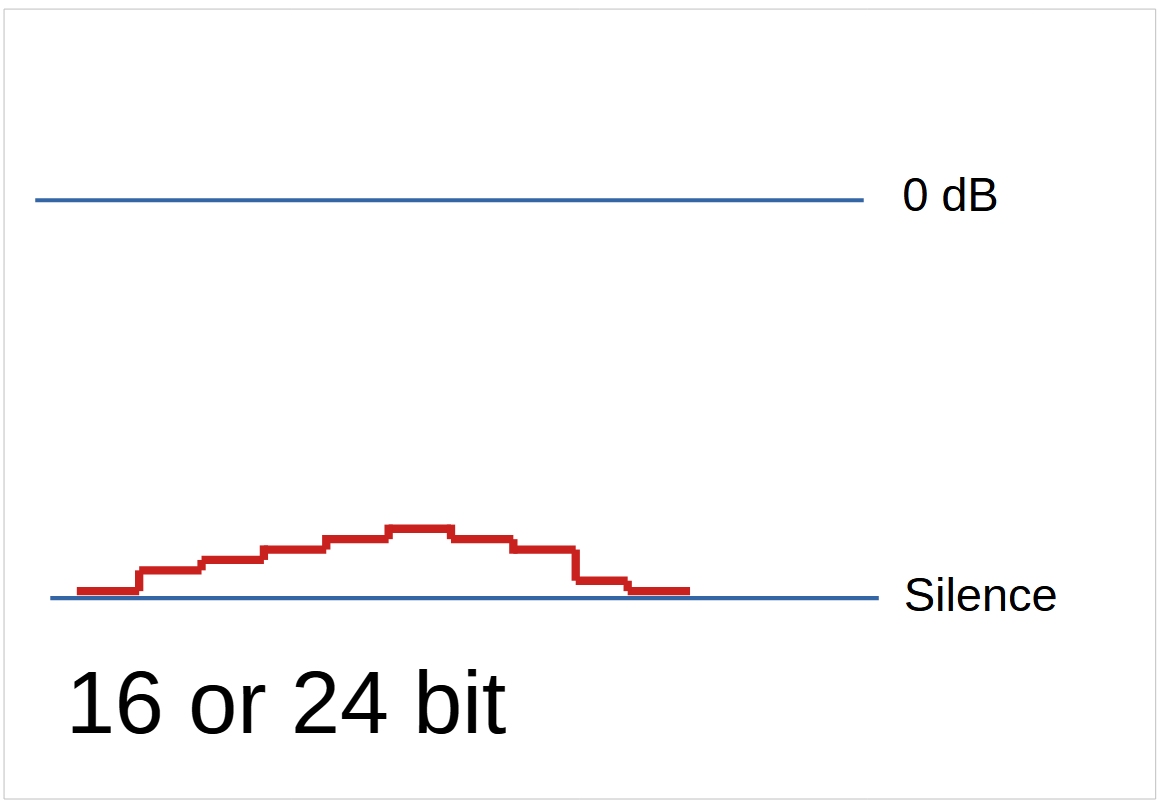
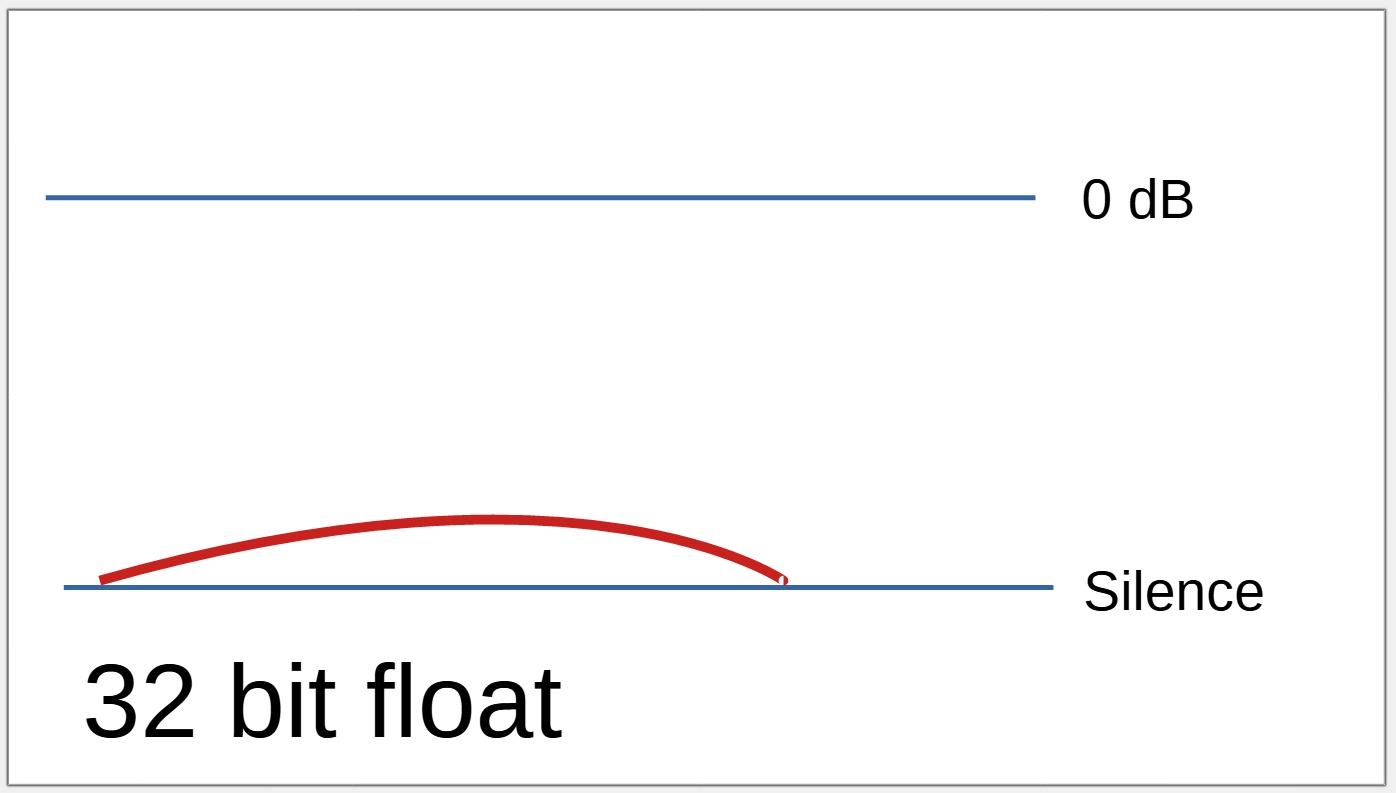
A very low level recording using 16 or 24 bit will have compromised quality when the level is increased.
A 32 bit float recording will sound perfect.

| Sample Resolution | Number of possible amplitude values | Dynamic Range | Stereo WAV file size per hour of audio |
| 16 bit | 24 bit | 32 bit integer | 32 bit float |
| 65,536 | 16,777,216 | 4,294,967,296 | 4,294,967,296 |
| 96 dB | 144 dB | 192 dB | 1,528 dB |
| 659 MB | 988 MB | 1,310 MB | 1,310 MB |
The resulting file size of a 32 bit recording will be approximately 1.3 times larger than a standard 24 bit recording.